In this article we will run our web application on multi-node swarm cluster.
You may want to read the previous articles:
- Hello Docker Macos Host
- Hello Docker With Docker Machine
- Run your first docker service/stack with swarm (Mono node)
Create 2 vms with docker-machine
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox <machine name>
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox machine1
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox machine2
List your vms (and get their ips)
docker-machine ls
Initiate your swarm manager on one of the vms
docker-machine ssh <machine name> "docker swarm init --advertise-addr <myvm1 ip>"
docker-machine ssh machine1 "docker swarm init --advertise-addr 192.168.99.105"
OR
eval $(docker-machine env machine1)
docker swarm init --advertise-addr <myvm1 ip>
docker swarm init --advertise-addr 192.168.99.105
Add a swarm worker to your swarm cluster (the join command is returned by the “swarm init” command above)
docker-machine ssh machine2 "docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-4udgeg63gvom4fliqgomj2vk25zf1mnk03l5yz0stb9cc4y6ft-9q938913xdtt4eymor8d186oq 192.168.99.105:2377"
OR
eval $(docker-machine env machine2)
docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-4udgeg63gvom4fliqgomj2vk25zf1mnk03l5yz0stb9cc4y6ft-9q938913xdtt4eymor8d186oq 192.168.99.105:2377
View the nodes in the swarm
docker-machine ssh machine1 "docker node ls"
To leave swarm, you need to leave it from each node with
docker swarm leave
Only swarm managers like machine1 execute Docker commands; workers are just for capacity. Deploy your application from machine1 with the same compose-yml that we have used previously. We will use the “docker-machine env” command before deploying our stack because it allows you to use your local docker-compose.yml file to deploy the stack “remotely” without having to copy it anywhere. Otherwise you can use “docker-machine scp
> eval $(docker-machine env machine1)
> docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml myApp
Creating network myApp_webnet
Creating service myApp_web
Note: If your image is stored on a private registry instead of Docker Hub, you need to be logged in using docker login <your-registry> and then you need to add the –with-registry-auth flag to the above command. For example:
docker login myregistry.example.com docker stack deploy --with-registry-auth -c docker-compose.yml myApp
List the replicated containers of your myApp_web service
> eval $(docker-machine env machine1)
> docker service ps myApp_web
ID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE ERROR PORTS
yp8nldzgaclu myApp_web.1 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine1 Running Running about a minute ago
mz30tjee1e32 myApp_web.2 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine2 Running Running 33 seconds ago
mll62ap0cvt1 myApp_web.3 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine2 Running Running 33 seconds ago
ly087nai6eia myApp_web.4 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine1 Running Running about a minute ago
i7ejraewwcge myApp_web.5 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine2 Running Running 33 seconds ago
Or list all the containers of the services of your myApp stack.
> eval $(docker-machine env machine1)
> docker stack ps myApp
ID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE ERROR PORTS
b7uavyisdyh6 myApp_web.1 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine1 Running Running about a minute ago
2zl5w78r4ql8 myApp_web.2 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine2 Running Running about a minute ago
vhvc3o5oypdv myApp_web.3 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine1 Running Running about a minute ago
wgwh6jbv3f0e myApp_web.4 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine2 Running Running about a minute ago
z8azc6dq1jvw myApp_web.5 legabz/hellokube:swagger machine2 Running Running about a minute ago
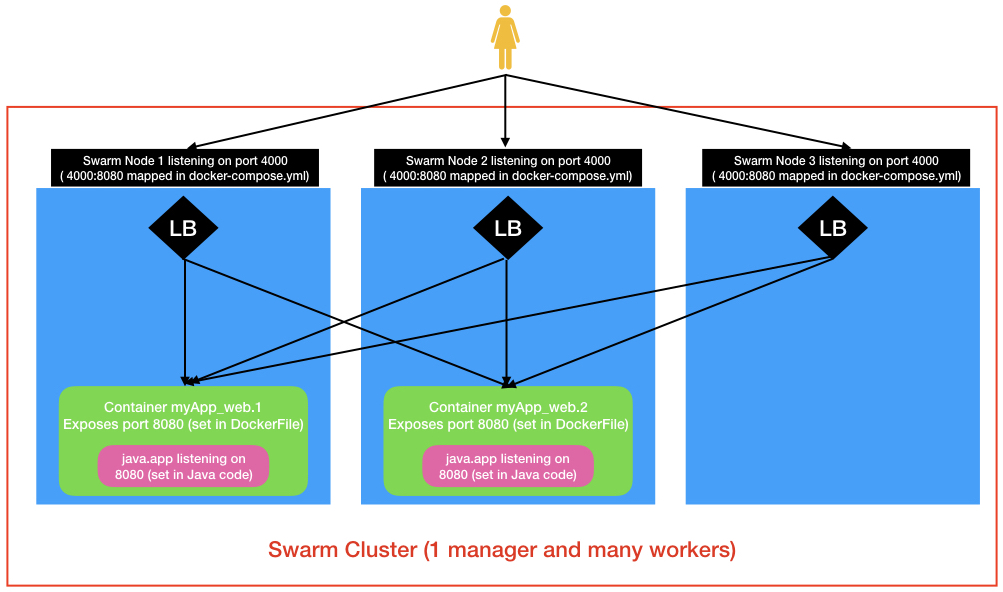
Yo may access your application using either of your swarm nodes ip. (http://192.168.99.105:4000/swagger-ui.html or http://192.168.99.105:4000/swagger-ui.html). All swarm nodes have a load balancer listening on the mapped port (set in the docker-compose.yml). These load balancers will redirect your request to one of the replicated containers which are listening on the exposed port (set in the DockeFile).
Some tips
Cheat sheet
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox myvm1 # Create a VM (Mac, Win7, Linux)
docker-machine create -d hyperv --hyperv-virtual-switch "myswitch" myvm1 # Win10
docker-machine env myvm1 # View basic information about your node
docker-machine ssh myvm1 "docker node ls" # List the nodes in your swarm
docker-machine ssh myvm1 "docker node inspect <node ID>" # Inspect a node
docker-machine ssh myvm1 "docker swarm join-token -q worker" # View join token
docker-machine ssh myvm1 # Open an SSH session with the VM; type "exit" to end
docker node ls # View nodes in swarm (while logged on to manager)
docker-machine ssh myvm2 "docker swarm leave" # Make the worker leave the swarm
docker-machine ssh myvm1 "docker swarm leave -f" # Make master leave, kill swarm
docker-machine ls # list VMs, asterisk shows which VM this shell is talking to
docker-machine start myvm1 # Start a VM that is currently not running
docker-machine env myvm1 # show environment variables and command for myvm1
eval $(docker-machine env myvm1) # Mac command to connect shell to myvm1
& "C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\Resources\bin\docker-machine.exe" env myvm1 | Invoke-Expression # Windows command to connect shell to myvm1
docker stack deploy -c <file> <app> # Deploy an app; command shell must be set to talk to manager (myvm1), uses local Compose file
docker-machine scp docker-compose.yml myvm1:~ # Copy file to node's home dir (only required if you use ssh to connect to manager and deploy the app)
docker-machine ssh myvm1 "docker stack deploy -c <file> <app>" # Deploy an app using ssh (you must have first copied the Compose file to myvm1)
eval $(docker-machine env -u) # Disconnect shell from VMs, use native docker
docker-machine stop $(docker-machine ls -q) # Stop all running VMs
docker-machine rm $(docker-machine ls -q) # Delete all VMs and their disk images